每一件美好的事情,开始都是困难的。——斯宾塞
Cartisan 是我五六年前取的名字,那时老罗刚开始搞手机,叫 Smartisan,我一直比较认同他提的一些价值观,所以就依葫芦画瓢,取了个 Cartisan,Code artisan,意为代码工匠。
我在【开篇】里说过,我要做一个系统,把自己学习的知识串起来,积累成一个产品,并且把这个过程通过博客的方式记录下来。
以前根据自己的工作情况,想写过不少类型的系统。我现在选择做一个电商系统,一是因为电商业务大家都比较了解,技术覆盖面够广,二是在开源社区有比较成熟的系统可参考。
现阶段业务逻辑主要参考 mall。
Cartisan 实践清单
根据我个人学习掌握的知识,我将在 Cartisan 上做以下实践,且不限于列表中的技术。
- 实例化需求
- 领域驱动设计
- 测试驱动开发
- 分布式、微服务系统架构
- DevOps
架构
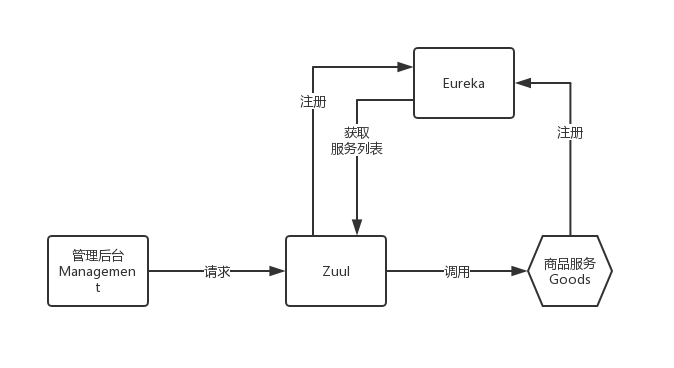
Cartisan 将使用前后端分离的架构,这个架构图我会在后面的开发过程中不断演化丰富。
现在的结构非常简单,管理后台向 Zuul 做的网关发送对商品服务的请求,Zuul 本身注册在 Eureka 做的注册中心上,并且从注册中心获取注册的服务列表,然后把请求转发给商品服务。
行走的骨架
程序员很多时候被称作 CRUD boy 不是没理由的,毕竟大多业务就是简单的 CRUD。
这里以商品品牌维护为例,通过简单的 CRUD,来走通这个简单的架构思路。目的有二:
- 不管简单或复杂,系统先得跑起来,才能不断演化。
- 从系统展现到服务逻辑实现,大部分功能就可以通过这种模式化的方式,实现快速开发。
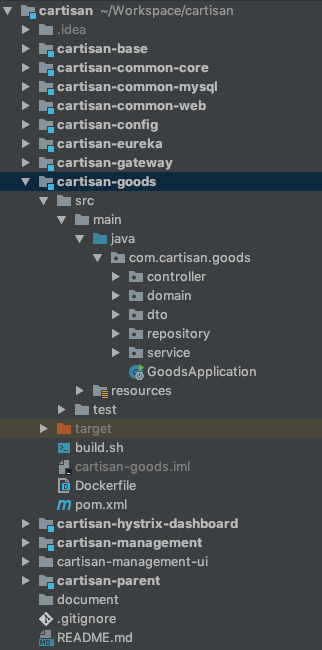
common-core、common-mysql、common-web 三个是 Cartisan 的基础库,一些通用的类,框架层面的基类、持久化处理、日志等等都在这里,每一个以后都单独整理说明。
Zuul 做的网关和商品服务都会向 Eureka 注册,这样就可以通过网关地址在服务名称完成对服务的访问。
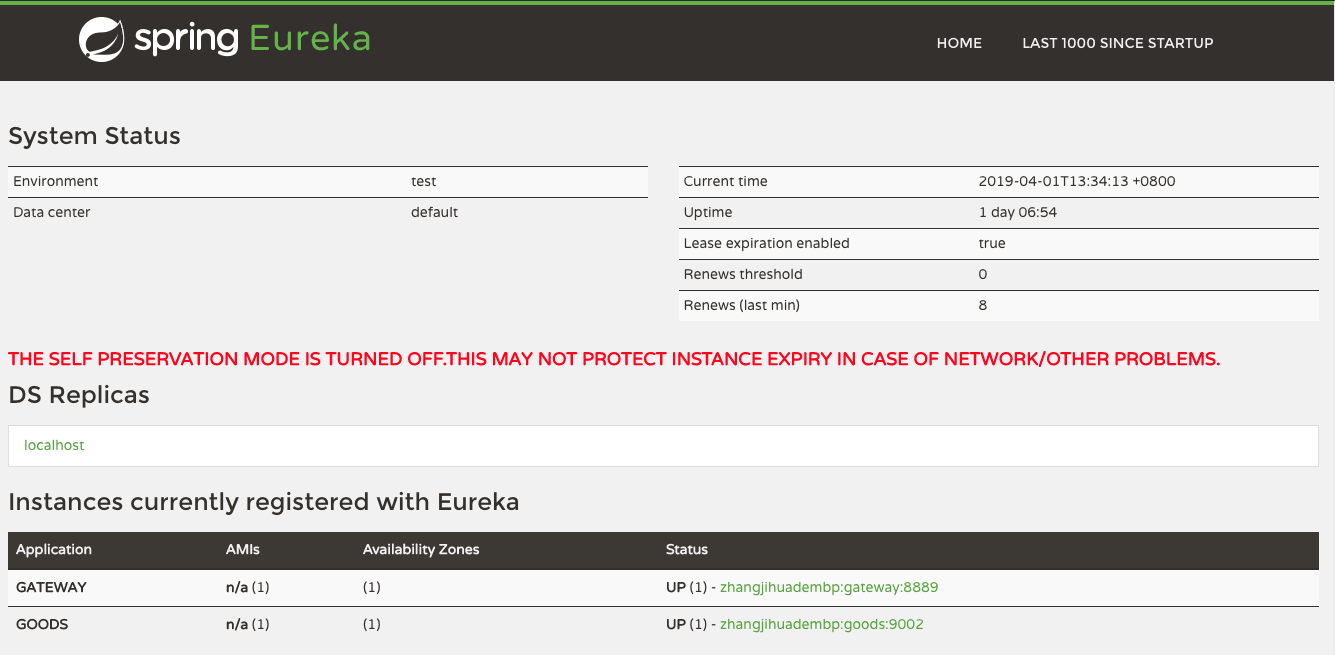
后端服务
pom.xml
pom 文件比较简单,根据业务场景,引入对应的基础库,基础库已经包含了所有要使用的其它依赖。
<dependencies>
<!-- cartisan 基础库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.cartisan</groupId>
<artifactId>cartisan-common-web</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.cartisan</groupId>
<artifactId>cartisan-common-mysql</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
应用入口
每个服务都是基于 Spring boot、Spring cloud 构建,CartisanApplication 是基于这两者构建基类,减少应用的重复配置及扫描基础库。
public class GoodsApplication extends CartisanApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(GoodsApplication.class);
}
@Bean
public IdWorker idWorker() {
return new IdWorker(1, 1);
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
@SpringCloudApplication
@ComponentScan(value = "com.cartisan.common")
public class CartisanApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(this.getClass());
}
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean hystrixStreamServlet() {
final HystrixMetricsStreamServlet hystrixMetricsStreamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
final ServletRegistrationBean<HystrixMetricsStreamServlet> registrationBean =
new ServletRegistrationBean<>(hystrixMetricsStreamServlet);
// 系统启动时的加载顺序
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
}
resources
- 配置
每个服务的配置,都根据生产、测试、开发等环境进行拆分。bootstrap 的配置是最优先加载的,所以使用 bootstrap 可以很好解决当使用配置中心时,对配置中心的配置及优先于配置中心的配置。
- SQL
微服务或者说一个限界上下文都应该独立的数据库,所以把每个服务的建库建表及初始化语句单独存放。
- api 测试
服务最重要的一点是测试,一般可以使用 PostMan,但访问请求的管理是个问题。IDEA 的 HttpClient 插件很好的解决了这个问题,把请求保存到一个 .http 文件中,在 IDEA 中就可以直接完成请求测试。
### 获取所有品牌列表
GET http://localhost:9002/brands
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
### 获取品牌
GET http://localhost:9002/brands/1
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
### 搜索品牌(不带参数)
GET http://localhost:9002/brands/search/1/10
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
### 搜索品牌
GET http://localhost:9002/brands/search/1/10?name=car
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
### 添加品牌
POST http://localhost:9002/brands
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"name": "cartisan",
"firstLetter": "C",
"isManufacturer": true,
"isShow": true,
"logo": "logo",
"bigPic": "bigPic",
"sort": 100
}
### 修改车型
PUT http://localhost:9002/brands/11
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"name": "cartisan",
"firstLetter": "C",
"isManufacturer": true,
"isShow": true,
"logo": "logo1",
"bigPic": "bigPic1",
"sort": 100
}
### 删除车型
DELETE http://localhost:9002/brands/11
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
###
领域模型与仓储
一般情况下领域模型承担了 DO 与 PO 的职责。ORM 选用 JPA 自带的 Hibernate 来完成。AbstractEntity 提供了常用的创建、更新时间的记录及软删除的支持。
@Entity
@Table(name = "goods_brands")
@Where(clause = "active=1 and deleted=0")
@Data
public class Brand extends AbstractEntity {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "first_letter")
private String firstLetter;
@Column(name = "is_manufacturer")
private Boolean isManufacturer;
@Column(name = "is_show")
private Boolean isShow;
@Column(name = "logo")
private String logo;
@Column(name = "big_pic")
private String bigPic;
@Column(name = "sort")
private Long sort;
}
public interface BrandRepository extends BaseRepository<Brand, Long> {
}
Service 与 Dto
服务一般以 Dto 作返回值,简单情况下,增改直接使用 Dto 传入,复杂业务场景,可以专门定义请求的 Parameter 对象。
@Service
public class BrandService {
@Autowired
private BrandRepository repository;
public List<BrandDto> findAllBrands() {
final List<Brand> brands = repository.findAll();
return brands.stream().map(BrandDto::convertFrom).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public BrandDto getBrand(Long id) {
return BrandDto.convertFrom(repository.findById(id).get());
}
public PageResult<BrandDto> searchBrands(String name, Integer currentPage, Integer pageSize) {
PageRequest pageRequest = PageRequest.of(currentPage - 1, pageSize,
new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "sort"));
final Page<Brand> searchResult = repository.findAll((Specification<Brand>) (root, query, criteriaBuilder) -> {
List<Predicate> predicateList = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(name)) {
predicateList.add(criteriaBuilder.like(root.get("name"),
"%" + name + "%"));
}
return criteriaBuilder.and(predicateList.toArray(new Predicate[predicateList.size()]));
}, pageRequest);
return new PageResult<>(searchResult.getTotalElements(),searchResult.getTotalPages(),
searchResult.map(BrandDto::convertFrom).getContent());
}
@Transactional(rollbackOn = Exception.class)
public void addBrand(BrandDto brandDto) {
final Brand brand = new Brand();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(brandDto, brand);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(brand.getFirstLetter())) {
brand.setFirstLetter(brand.getName().substring(0, 1));
}
repository.save(brand);
}
@Transactional(rollbackOn = Exception.class)
public void editBrand(Long id, BrandDto brandDto) {
final Brand brand = repository.findById(id).get();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(brandDto, brand);
brand.setId(id);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(brand.getFirstLetter())) {
brand.setFirstLetter(brand.getName().substring(0, 1));
}
// TODO: 更新品牌时要更新商品中的品牌名称
repository.save(brand);
}
@Transactional(rollbackOn = Exception.class)
public void removeBrand(long id) {
repository.deleteById(id);
}
}
Controller
Controller 统一使用 Restful 风格,每个接口包括参数,都打上 Swagger 的 annotation,便于生成接口文档。
@Api(tags = "BrandController", description = "商品品牌管理")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/brands")
public class BrandController {
@Autowired
private BrandService service;
@ApiOperation(value = "获取所有品牌列表")
@GetMapping
public GenericResponse<List<BrandDto>> findAllBrands() {
return success(service.findAllBrands());
}
@ApiOperation(value = "获取品牌")
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public GenericResponse<BrandDto> getBrand(
@ApiParam(value = "品牌Id", required = true) @PathVariable Long id) {
return success(service.getBrand(id));
}
@ApiOperation(value = "搜索品牌")
@GetMapping("/search/{currentPage}/{pageSize}")
public GenericResponse<PageResult<BrandDto>> searchBrands(
@RequestParam(required = false) String name,
@PathVariable Integer currentPage,
@PathVariable Integer pageSize) {
return success(service.searchBrands(name, currentPage, pageSize));
}
@ApiOperation(value = "添加品牌")
@PostMapping
public GenericResponse addBrand(
@ApiParam(value = "品牌信息", required = true) @RequestBody BrandDto brandDto) {
service.addBrand(brandDto);
return success();
}
@ApiOperation(value = "更新品牌")
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public GenericResponse editBrand(
@ApiParam(value = "品牌Id", required = true) @PathVariable Long id,
@ApiParam(value = "品牌信息", required = true) @RequestBody BrandDto brandDto) {
service.editBrand(id, brandDto);
return success();
}
@ApiOperation(value = "删除品牌")
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public GenericResponse removeBrand(
@ApiParam(value = "品牌Id", required = true) @PathVariable long id) {
service.removeBrand(id);
return success();
}
}
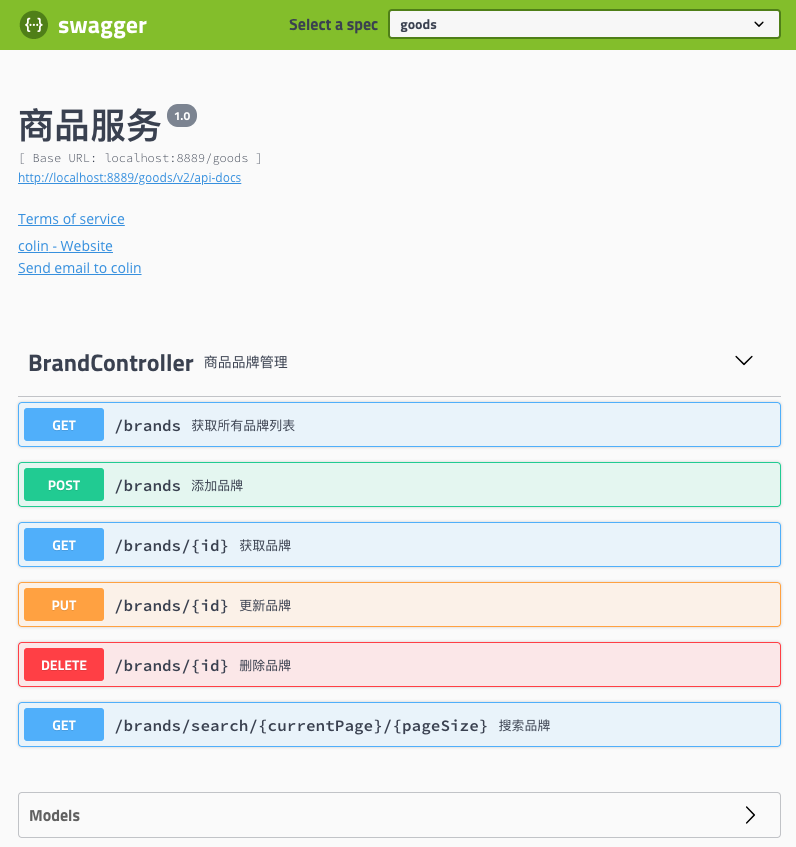
前端(管理后台)
管理后台使用强大的 vue-element-admin 做模板。
Api
为每个后台服务创建一个使用 axios 进行远程访问的服务代理。访问服务的基地址就是网关提供的地址。
module.exports = {
NODE_ENV: '"development"',
ENV_CONFIG: '"dev"',
// BASE_API: '"https://api-dev"'
BASE_API: '"http://localhost:8889"'
}
import request from '@/utils/request';
export function searchBrands(currentPage, pageSize, params) {
return request({
url: `/goods/brands/search/${currentPage}/${pageSize}`,
method: 'get',
params: params
});
}
export function findAllBrands() {
return request({
url: '/goods/brands',
method: 'get'
});
}
export function getBrand(id) {
return request({
url: `/goods/brands/${id}`,
method: 'get'
});
}
export function addBrand(params) {
return request({
url: '/goods/brands',
method: 'post',
data: params
});
}
export function editBrand(id, params) {
return request({
url: `/goods/brands/${id}`,
method: 'put',
data: params
});
}
export function removeBrand(id) {
return request({
url: `/goods/brands/${id}`,
method: 'delete'
});
}
路由
为了便于管理,每个模块使用单独的配置文件。不需要显示到菜单上的,配置 hidden: true。
import Layout from '@/views/layout/Layout';
const goods = {
path: '/goods',
component: Layout,
redirect: '/goods/brand',
name: 'Goods',
meta: {
title: '商品',
icon: 'clipboard'
},
children: [
{
path: 'brand',
name: 'Brand',
component: () => import('@/views/goods/brands'),
meta: { title: '品牌管理' }
},
{
path: 'brandAdd',
name: 'BrandAdd',
component: () => import('@/views/goods/brandAdd'),
meta: { title: '添加品牌' },
hidden: true
},
{
path: 'brandEdit',
name: 'BrandEdit',
component: () => import('@/views/goods/brandEdit'),
meta: { title: '编辑品牌' },
hidden: true
}
]
};
export default goods;
页面
页面统一建立在 views 目录下,一般的 CRUD,可以模式化地建成列表、新增、更新及一个表单组件。
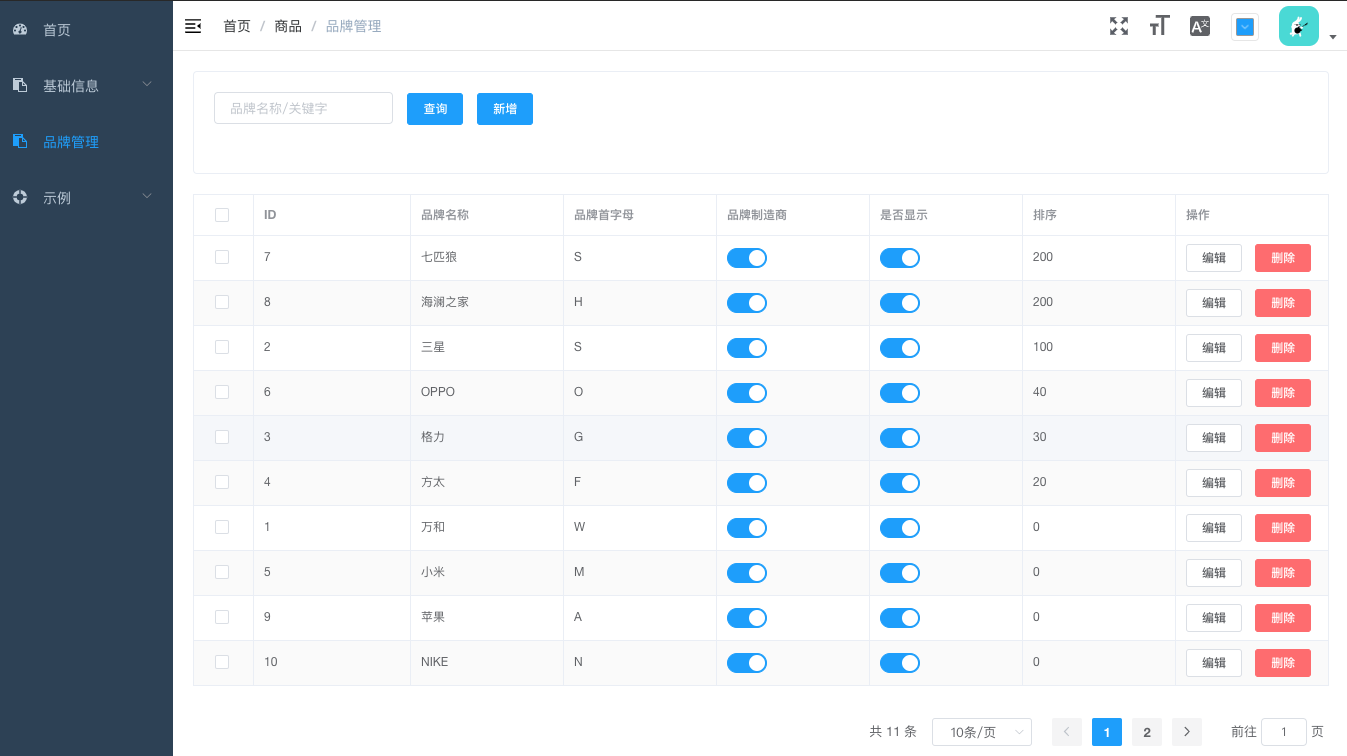
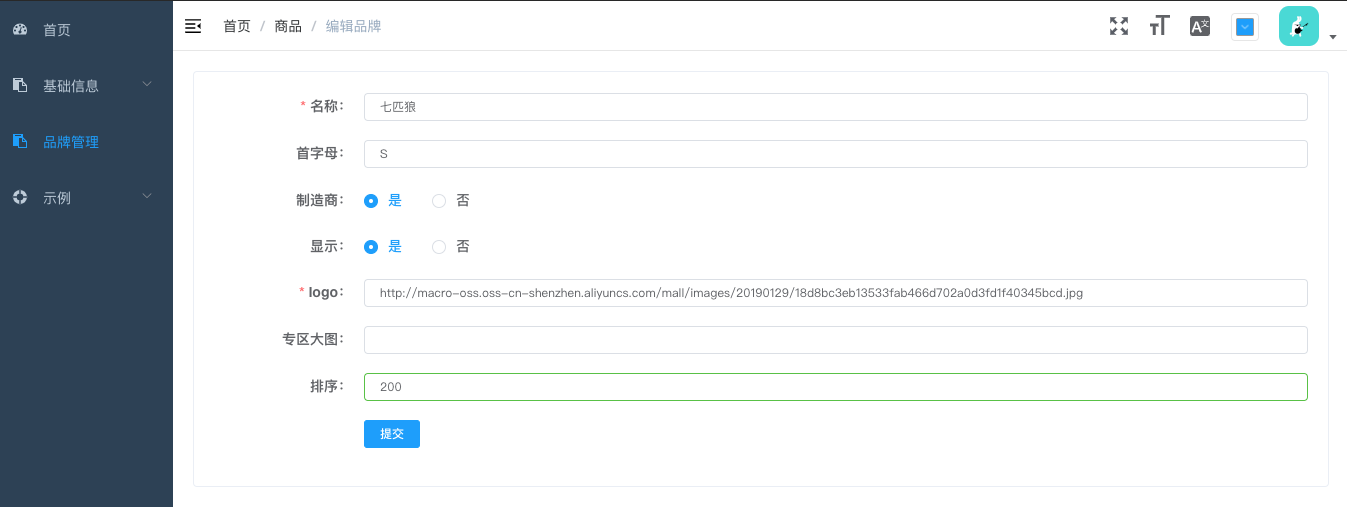
运行效果
- 列表页
- 编辑页
总结
至此,一个简单的前后端分离的系统就搭建完成了。对于简单的一些业务功能,完全可以套用这样的结构快速完成。
当然,在基础库及系统流程上还需要不断完善增强,包括领域驱动在代码层面的落地,分布式架构下各种问题的应对,后面会一步步改进。